Group Policy
- Details
- Category: Windows Serwer 2019
- Published: Sunday, 18 August 2024 15:47
- Written by admin4830
- Hits: 163
Linki do przykładów
https://www.firewall.cx/operating-systems/microsoft/windows-servers/windows-2012-group-policies.html'
OK
https://blog.netwrix.com/group-policy-management#Introduction_to_Group_Policy_Management
OK BAD
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SD9HtdYOmMs&ab_channel=ServerAcademy
https://activedirectorypro.com/group-policy-examples-most-useful-gpos-for-security/
https://www.lepide.com/blog/top-10-most-important-group-policy-settings-for-preventing-security-breaches/
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/top-12-group-policy-settings-preventing-security-breaches-politis-3tthf
https://www.cayosoft.com/active-directory-management-tools/active-directory-group-policy-management/
Ważne zmiany konfiguracyjne:
Zmiana nazwy serwera kontrolera domeny na DC1 – ścieżki sieciowe
Komendy
Aktualizacja
GPO na stacji roboczej
gpupdate /force
Display
All Applied GPOs applied to (User and Computer)
gpresult /r
Display
GPOs applied to a specific user
gpresult /r /scope:user
Display
GPOs applied to a specific computer
gpresult /r /scope:computer
Display
GPOs applied on a remote computer
gpresult /s pc2 /r
Generate
HTML Report
gpresult /h c:\reports.html
Export
to a text file
gpresult /r >c:\results.txt
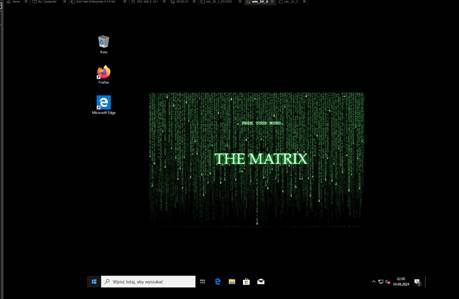
Zdjęcie background
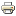
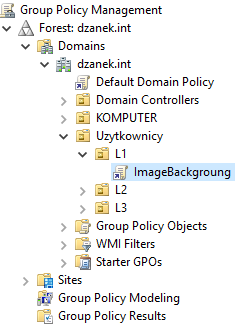
Tworzymy nową GPO

Nazwa: ImageBackground

Group Policy Manager
Editor
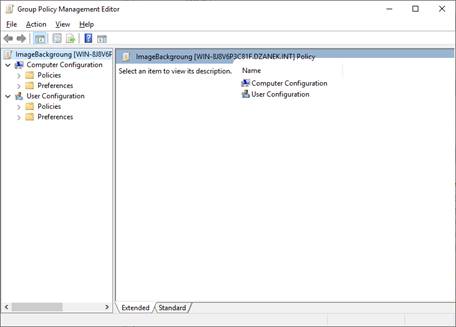
User Configuration>
Policies> Administrative Templates> Desktop> Desktop -> Desktop
Wallpaper
Zdjęcie na desktop
umieszczamy w zasobie udostępnionym dla użytkowników.

GPO Polityka dotyczy
użytkowników – została dodana do kontenera z użytkownikami
Polityka dotyczy
użytkowników tylko z kontenera L1
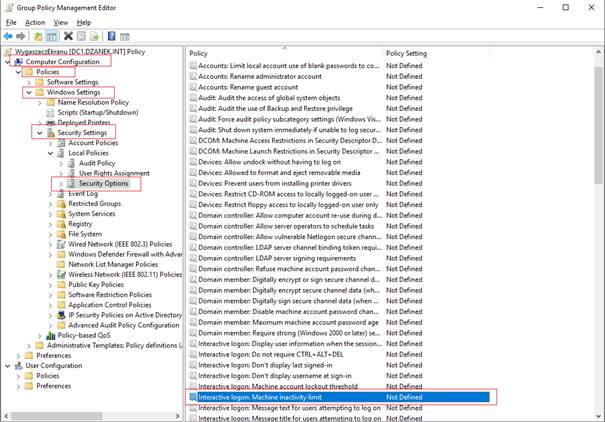
Wygaszacz Ekranu
Computer Configuration
->Polices-> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Local Policies
-> Security Options:
“Interactive Logon:
Machine inactivity limit”

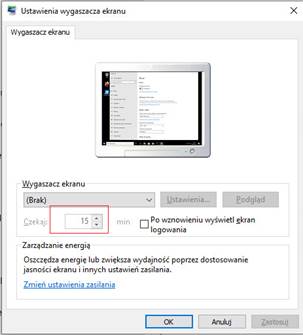
Change the value to
whatever you want. I set mine to 900 seconds which is 15 minutes.
Czas ustawiamy w sekundach
Sprawdzamy ustawienia wygaszacza na stacji roboczej
Sprawdzamy na stacji roboczej jakie GPO dotyczą komputera
gpresult /r /scope:computer
![]()
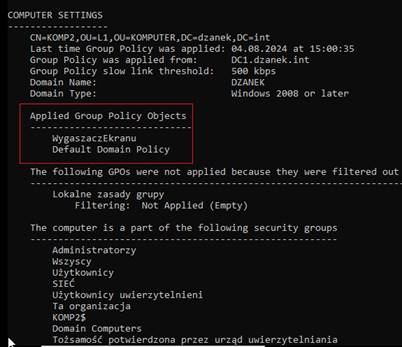
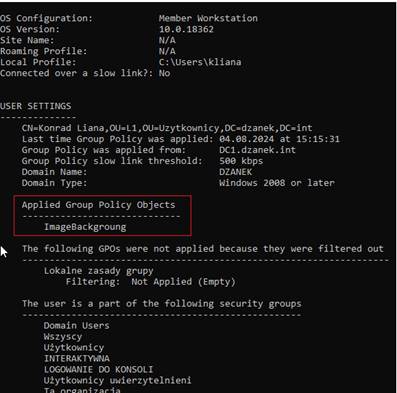
Sprawdzamy na stacji roboczej jakie
GPO dotyczą użytkownika
gpresult /r /scope:user
![]()
Account Logon
Configure Audit Policy for
Active Directory (For all Domain Controllers)
By default, there is a bare
minimum audit policy configured for Active Directory. You will need to modify
the default domain controller policy or create a new one.
Follow these steps to
enable an audit policy for Active Directory.
Computer Configuration
-> Polices->Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Advanced Policy
Configuration
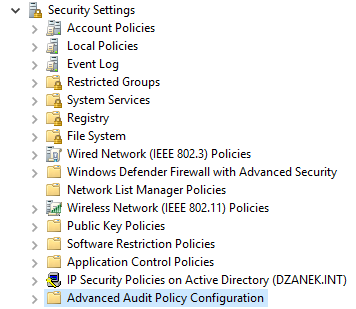
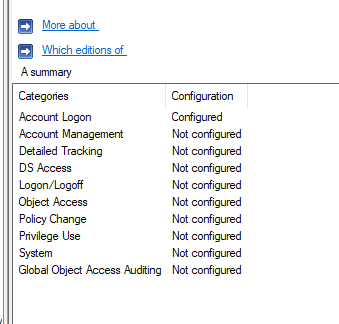
Account Logon
Recommended Audit Policy
Settings
These settings are from the
MS Security baseline Windows 10 and Server 2016 document.
Recommended domain
controller security and audit policy settings.
GPO Policy location:
Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security
Settings -> Advanced Audit Policy Configuration
Account Logon
- Audit Credential Validation
- Success and Failure
- Audit Kerberos Authentication Services
- Not configured
- Audit Kerberos Service Ticket Operations
- Not configured
- Audit Other Account Logon Events
- Not configured
Account Management
- Audit Application Group Management
- Not configured
- Audit Computer Account Management
- Success
- Audit Distribution Group Management
- Not configured
- Audit Other Account Management Events
- Success and Failure
- Audit Security Group Management
- Success and Failure
- Audit User Account Management
- Success and Failure
Detailed Tracking
- Audit DPAPI Activity
- Not configured
- Audit Plug and Play Events
- Success
- Audit Process Creation
- Success
- Audit Process Termination
- Not Configured
- Audit RPC Events
- Not Configured
- Audit Token Right Adjected
- Not Configured
DS Access
- Audit Detailed Directory Service Replication
- Not configured
- Audit Directory Service Access
- Success and Failure
- Audit Directory Service Changes
- Success and Failure
- Audit Directory Service Replication
- Not Configured
Logon/Logoff
- Audit Account Lockout
- Success and Failure
- Audit User / Device Claims
- Not configured
- Audit Group Membership
- Success
- Audit IPsec Extended Mode
- Not configured
- Audit IPsec Main Mode
- Not configured
- Audit Logoff
- Success
- Audit Logon
- Success and Failure
- Audit Network Policy Server
- Not configured
- Audit Other Logon/Logoff Events
- Not configured
- Audit Special Logon
- Success
Object Access
- Audit Application Generated
- Not configured
- Audit Certification Services
- Not configured
- Audit Detailed File Share
- Not configured
- Audit File Share
- Not configured
- Audit File System
- Not configured
- Audit Filtering Platform Connection
- Not configured
- Audit Filtering Platform Packet Drop
- Not configured
- Audit Handle Manipulation
- Not configured
- Audit Kernal Object
- Not configured
- Audit Other Object Access Events
- Not configured
- Audit Registry
- Not configured
- Audit Removable Storage
- Success and Failure
- Audit SAM
- Not configured
- Audit Central Access Policy Staging
- Not configured
Policy Change
- Audit Audit Policy Change
- Success and Failure
- Audit Authentication Policy Change
- Success
- Audit Authorization Policy Change
- Success
- Audit Filtering Platform Policy Change
- Not configured
- Audit MPSSVC Rule-Level Policy
Change
- Not Configured
- Audit Other Policy Change Events
- Not configured
Privilege Use
- Audit Non Sensitive Privilege Use
- Not configured
- Audit Other Privilege Use Events
- Not configured
- Audit Sensitive Privilege Use
- Success and Failure
System
- Audit IPsec Driver
- Success and Failure
- Audit Other System Events
- Success and Failure
- Audit Security State Change
- Success
- Audit Security System Extension
- Success and Failure
- Audit System Integrity
- Success and Failure
Global Object Access Auditing
- File System
- Not configured
- Registry
- Not configured
- Account Management
- Detailed Tracking
- DS Access
- Logon/Logoff
- Object Access
- Policy Change
- Privilege Use
- System
- Global Object Access Auditing
I
recommend you download the Microsoft
Security compliance toolkit. It has an Excel document with recommended security and audit settings
for Windows 10, member servers, and domain controllers. I’ve also created an AD
Audit Checklist for
a quick reference on the recommended audit policy settings.
Centralize Windows Event Logs
When you enable a
security and audit policy on all systems those event logs are stored locally on
each system. When you need to investigate an incident or run audit reports you
will need to go through each log individually on each computer. Another concern
is what if a system crashes and you are unable to access the logs?
and… don’t forget those
local logs are intended for short term storage. In large environments, those
local logs will be overwritten by new events in a short period of time.
Centralizing your logs
will save you time, ensure logs are available, and make it easier to report and
troubleshoot security incidents. There are many tools out there that can
centralize Windows event logs.
Below is a list of free
and premium tools that will centralize Windows event logs. Some of the free
tools require a bit of work and may require additional software to visualize
and report on the logs. If you have the budget I recommend a premium tool, they
are much easier to setup and saves you a ton of time.
- SolarWinds Log Analyzer (Premium tool,
30-day FREE trial)
- Windows
Event Collector (Free, requires additional tools to visualize
and report on data)
- ManageEngine
Audit Plus – (Premium tool)
- Splunk – (Premium tool, a popular tool for
analyzing various log files)
- Elastic
Stack – (Free download)